3.8 KiB
Flutter devicelab
"Devicelab" (a.k.a. "cocoon") is a physical lab that tests Flutter on real Android and iOS devices.
This package contains the code for test framework and the tests. More generally the tests are referred to as "tasks" in the API, but since we primarily use it for testing, this document refers to them as "tests".
You can see the continuous build results from the master branch at http://go/flutter-dashboard/build.html.
Running tests locally
Do make sure your tests pass locally before deploying to the CI environment. Below is a handful of commands that run tests in a similar way to how the CI environment runs them. These commands are also useful when you need to reproduce a CI test failure locally.
To run a test, use option -t (--task):
dart bin/run.dart -t {NAME_OF_TEST}
To run multiple tests, repeat option -t (--task) multiple times:
dart bin/run.dart -t test1 -t test2 -t test3
To run all tests defined in manifest.yaml, use option -a (--all):
dart bin/run.dart -a
To run tests from a specific stage, use option -s (--stage):
dart bin/run.dart -s {NAME_OF_STAGE}
Reproducing broken builds locally
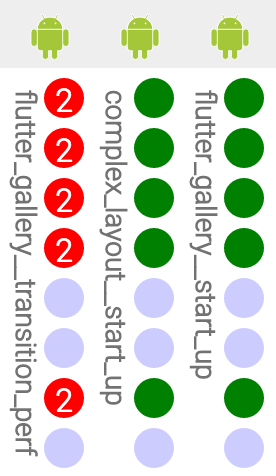
If a commit caused a test to fail, the dashboard might look something like this:
The red circle tells you that a test failed. The number inside tells you how many times the devicelab attempted to run the test before giving up on it.
To reproduce the breakage locally git checkout the corresponding Flutter
revision. Note the name of the test that failed. In the example above the
failing test is flutter_gallery__transition_perf. This name can be passed to
the run.dart command. For example:
dart bin/run.dart -t flutter_gallery__transition_perf
Writing tests
A test is a simple Dart program that lives under bin/tests and uses
package:flutter_devicelab/framework/framework.dart to define and run a task.
Example:
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter_devicelab/framework/framework.dart';
Future<Null> main() async {
await task(() async {
... do something interesting ...
// Aggregate results into a JSONable Map structure.
Map<String, dynamic> testResults = ...;
// Report success.
return new TaskResult.success(testResults);
// Or you can also report a failure.
return new TaskResult.failure('Something went wrong!');
});
}
Only one task is permitted per program. However, that task can run any number
of tests internally. A task has a name. It succeeds and fails independently of
other tasks, and is reported to the dashboard independently of other tasks.
A task runs in its own standalone Dart VM and reports results via Dart VM service protocol. This ensures that tasks do not interfere with each other and lets the CI system time out and clean up tasks that get stuck.
Adding tests to the CI environment
The manifest.yaml file describes a subset of tests we run in the CI. To add
your test edit manifest.yaml and add the following in the "tasks" dictionary:
{NAME_OF_TEST}:
description: {DESCRIPTION}
stage: {STAGE}
required_agent_capabilities: {CAPABILITIES}
Where:
{NAME_OF_TEST}is the name of your test that also matches the name of the file inbin/testswithout the.dartextension.{DESCRIPTION}is the plain English description of your test that helps others understand what this test is testing.{STAGE}isdevicelabif you want to run on Android, ordevicelab_iosif you want to run on iOS.{CAPABILITIES}is an array that lists the capabilities required of the test agent (the computer that runs the test) to run your test. Available capabilities are:has-android-device,has-ios-device.